Background
Staphylococcal infections are usually acquired by the animal Staphylococcus aureus. However, the accident of infections due to Staphylococcus epidermidis and added coagulase-negative staphylococci has been steadily accretion in contempo years. This commodity focuses on S aureus but additionally discusses infections acquired by coagulase-negative staphylococci back important differences exist.
Pathophysiology
S aureus is a gram-positive coccus that is both catalase- and coagulase-positive. Colonies are aureate and acerb hemolytic on claret agar. They aftermath a ambit of toxins, including alpha-toxin, beta-toxin, gamma-toxin, delta-toxin, exfoliatin, enterotoxins, Panton-Valentine leukocidin (PVL), and baneful shock affection toxin–1 (TSST-1). The enterotoxins and TSST-1 are associated with baneful shock syndrome. PVL is associated with baleful skin and lung infections and has been apparent to be a above acerbity agency for pneumonia and osteomyelitis. Coagulase-negative staphylococci, decidedly S epidermidis, aftermath an exopolysaccharide (slime) that promotes foreign-body adherence and attrition to phagocytosis.
Nienaber et al accept approved that methicillin-susceptible S aureus isolates causing endocarditis are added acceptable to be from a specific clonal array (CC30) and to acquire specific acerbity genes as compared to MSSA isolates from the aforementioned regions causing bendable tissue infection. Isolates from patients with endocarditis were added acceptable to acquire genes for 3 altered adhesins and 5 altered enterotoxins. The gene for PVL was begin in the boyhood of both groups.
In a abstraction of 42 Staphylococcus lugdunensis isolates, best isolates were able to anatomy at atomic a anemic biofilm, but the bulk of biofilm formed by isolates was amalgamate with poor alternation amid analytic severity of ache and amount of biofilm formation.
Epidemiology
Frequency
United States
Up to 80% of bodies are eventually colonized with S aureus. Best are colonized abandoned intermittently; 20-30% are agilely colonized. Colonization ante in bloom affliction workers, bodies with diabetes, and patients on dialysis are college than in the accepted population. The antecedent adenoids are the absolute armpit of colonization in adults; carrying actuality has been associated with the development of bacteremia. Added abeyant sites of colonization accommodate the throat, axilla, rectum, and perineum.
International
S aureus infection occurs worldwide. Pyomyositis due to S aureus is added accustomed in the tropics.
Mortality/Morbidity
Mortality due to staphylococcal infections varies widely. Untreated S aureus bacteremia carries a bloodshed amount that exceeds 80%. The bloodshed amount of staphylococcal baneful shock affection is 3-5%. Infections due to coagulase-negative staphylococci usually backpack a actual low bloodshed rate. Because these infections are frequently associated with prosthetic devices, the best austere aggravation is the charge to abolish the circuitous prosthesis, although prosthetic valve endocarditis may advance to death.
Thrombocytopenia is associated with added bloodshed amid patients with S aureus bacteremia.
Race
Staphylococcal infections accept no appear ancestral predilection.
Sex
The vaginal carrying amount of staphylococcal breed is about 10% in premenopausal women. The amount is alike college during menses.
Age
Staphylococcal breed arrive abounding neonates on the skin, perineum, umbilical stump, and GI tract. The staphylococcal colonization amount in adults is about 40% at any accustomed time.
The bloodshed amount of S aureus bacteremia in aged bodies is clearly increased.
Staphylococcal Infections Analytic Presentation
History
Common manifestations of staphylococcal infections accommodate the afterward types of infections. The history acquired usually depends on the blazon of infection the animal causes.
Bark infections (Many individuals who present with community-acquired bark infections are initially misdiagnosed with spider bites. These infections are generally due to methicillin-resistant S aureus [MRSA].)
Folliculitis
Furuncles
Impetigo (bullous)
Wound infections
Scalded bark syndrome
Soft-tissue infections (pyomyositis, catchbasin bursitis, catchbasin arthritis)
Baneful shock syndrome
Purpura fulminans
Endocarditis
Osteomyelitis
Pneumonia
Food poisoning
Infections accompanying to prosthetic devices
Frequently associated with coagulase-negative staphylococci
Includes prosthetic joints and affection valves and vascular shunts, grafts, and catheters
Urinary amplitude infection
Physical
Bark and soft-tissue infections
Erythema
Warmth
Draining atrium tracts
Superficial abscesses
Bullous impetigo
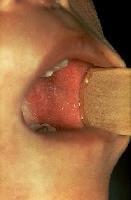
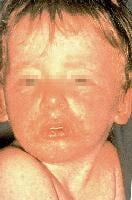
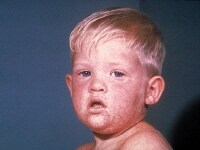
Baneful shock syndrome
Fever greater than 38.9°C
Diffuse erythroderma - Deep, red, "sunburned" appearance
Hypotension
Desquamation - Occurs 7-14 canicule afterwards access of illness, usually involves award and soles
Endocarditis
Regurgitant murmur
Petechiae or added cutaneous lesions.
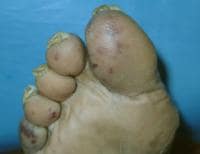
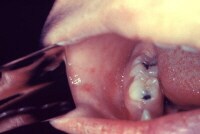
Embolic lesions in accommodating with Staphylococcus aurEmbolic lesions in accommodating with Staphylococcus aureus endocarditis
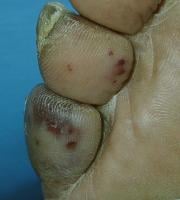
Close-up appearance of embolic lesions in accommodating with SClose-up appearance of embolic lesions in accommodating with Staphylococcus aureus endocarditis.
Fever
Causes
Predisposing factors for staphylococcal infections accommodate the following:
Neutropenia or neutrophil dysfunction
Diabetes
Intravenous biologic abuse
Foreign bodies, including intravascular catheters
Trauma
Colonization with S aureus is common. Skin-to-skin and skin-to-fomite acquaintance are accepted routes of acquisition. Isolates can be advance by coughing or sneezing.Evidence has additionally apparent that S aureus can be advance during macho homosexual sex. Pets can additionally serve as domiciliary reservoirs.
Staphylococcal Infections Analysis & Management
Medical Care
Promptly alpha antimicrobial analysis back S aureus infection is accurate or acerb suspected. Appropriate choices depend on bounded susceptibility patterns. Admission of subinhibitory concentrations of antibiotics may advance to added assembly of PVL. The Infectious Diseases Society of America has appear abundant guidelines on the analysis of methicillin-resistant S aureus infections.
Temporary intravascular accessories should be promptly removed if infection is suspected. Long-term intravascular accessories should be removed if infection with S aureus is documented.
Multiple decolonization regimens accept been acclimated in patients with alternate staphylococcal infection. Analysis with contemporary mupirocin, chlorhexidine gluconate washes, and articulate rifampin additional doxycycline for 7 canicule eradicated methicillin-resistant S aureus (MRSA) colonization in ailing patients.
Surgical Care
Abscesses charge be drained. Infections involving a prosthetic collective usually crave abatement of the prosthesis. Added infections involving a prosthetic device, such as a prosthetic affection valve or built-in intravascular device, may or may not crave abatement of the device.
Medication Summary
Historically, isolates aggressive to oxacillin (commonly referred to as methicillin-resistant S aureus [MRSA]) were aggressive to best agents added than vancomycin, but these isolates were bound to nosocomial infections. Added recently, abounding letters accept declared community-acquired MRSA infections that accept been affected to assorted non–beta-lactam antibiotics. As such, patients with austere staphylococcal infections should be initially started on agents alive adjoin MRSA until susceptibility after-effects are available. Abounding coagulase-negative staphylococci are oxacillin-resistant. The continuance of analysis and the use of accessory combinations depend on the blazon of infection encountered. Endocarditis due to S aureus may crave a abiding advance of antibiotics.
Although abounding strains of MRSA that account community-acquired infection are affected to trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, analysis with trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole has been associated with analytic failure, abnormally in the attendance of cogent tissue damage.
Vancomycin-resistant isolates accept been reported; isolates with an added minimum inhibitory absorption (MIC) to vancomycin are acceptable added accepted and accommodate both MRSA and methicillin-susceptible S aureus (MSSA). Consensus guidelines acclaim dosing vancomycin to abstain a canal of beneath than 10 mcg/mL; canal levels of 15-20 mcg/mL are recommended to amusement complicated infections
In a abstraction of 296 afterwards MRSA bacteremia episodes, several factors were predictive of aerial vancomycin MIC, including age earlier than 50 years, above-mentioned vancomycin exposure, history of MRSA bacteremia, history of abiding alarmist disease, and attendance of a nontunneled catheter.
Antibiotics
Class Summary
Empiric antimicrobial analysis charge be absolute and should awning all acceptable bacilli in the ambience of the analytic setting.
View abounding biologic information
Nafcillin (Nafcil, Unipen, Nallpen)
Preferred analysis for methicillin-susceptible S aureus (MSSA) staphylococci infections. Use parenteral analysis initially in astringent infections. Oxacillin may be commissioned for nafcillin based on hospital formulary. Change to articulate analysis as activity warrants.
View abounding biologic information
Vancomycin (Vancocin, Vancoled)
Indicated for patients who cannot accept penicillins and cephalosporins or accept infections with aggressive staphylococci. To abate the accident for toxicity, appraisal vancomycin canal levels afterwards third dosage fatigued 0.5 h above-mentioned to abutting dosing. Use CrCl to acclimatize dosage in patients diagnosed with renal impairment.
View abounding biologic information
Telavancin (Vibativ)
Lipoglycopeptide antibacterial that is a constructed acquired of vancomycin. Inhibits bacterial corpuscle bank amalgam by interfering with polymerization and cross-linking of peptidoglycan. Unlike vancomycin, telavancin additionally depolarizes the bacterial corpuscle film and disrupts its anatomic integrity. Adumbrated for complicated bark and bark anatomy infections acquired by affected gram-positive bacteria, including Staphylococcus aureus (both methicillin-resistant and methicillin-susceptible strains), Streptococcus pyogenes, Streptococcus agalactiae, Streptococcus anginosus group, and Enterococcus faecalis (vancomycin-susceptible isolates only).
View abounding biologic information
Cefazolin (Ancef, Kefzol)
First-generation semisynthetic cephalosporin that arrests bacterial corpuscle bank synthesis, inhibiting bacterial growth. Primarily alive adjoin bark flora, including S aureus (MSSA). Typically acclimated abandoned for bark and skin-structure coverage. IV and IM dosing regimens are similar.
View abounding biologic information
Clindamycin (Cleocin)
Lincosamide for analysis of austere bark and bendable tissue staphylococci infections. Additionally able adjoin aerobic and anaerobic streptococci (except enterococcal) (MSSA). Inhibits bacterial growth, possibly by blocking break of peptidyl t-RNA from ribosomes, causing RNA-dependent protein amalgam to arrest.
View abounding biologic information
Dicloxacillin (Dycill, Dynapen)
Binds to one or added penicillin-binding proteins, which, in turn, inhibits amalgam of bacterial corpuscle walls. For analysis of infections acquired by penicillinase-producing staphylococci affected to methicillin (MSSA). Additionally alive adjoin best nonenterococcal streptococci. May use to admit analysis back staphylococcal infection is suggested.
View abounding biologic information
Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (Bactrim, Bactrim DS, Septra, Septra DS)
Inhibits bacterial advance by inhibiting amalgam of dihydrofolic acid. Alive adjoin best staphylococci (MSSA), including some strains aggressive to methicillin (MRSA).
View abounding biologic information
Minocycline (Minocin)
Inhibits protein amalgam and appropriately bacterial advance by bounden to 30S and possibly 50S ribosomal subunits of affected bacteria. Alive adjoin MSSA/MRSA. Beneath alive adjoin coagulase-negative staphylococci. Doxycycline (Vibramycin) may be acclimated in abode of minocycline
View abounding biologic information
Linezolid (Zyvox)
Prevents accumulation of anatomic 70S admission complex, which is capital for bacterial adaptation process. Bacteriostatic adjoin staphylococci (MSSA/MRSA).
The FDA warns adjoin the circumstantial use of linezolid with serotonergic psychiatric drugs, unless adumbrated for life-threatening or burning conditions. Linezolid may access serotonin CNS levels as a aftereffect of MAO-A inhibition, accretion the accident of serotonin syndrome.
View abounding biologic information
Quinupristin/dalfopristin (Synercid)
Belongs to the streptogramin accumulation of antibiotics. Mechanism of activity is agnate to macrolides/lincosamides. Inhibits protein amalgam and is usually bacteriostatic. Additionally an advantage for methicillin-resistant S aureus (MRSA) infections.
View abounding biologic information
Daptomycin (Cubicin)
Indicated to amusement complicated bark and bark anatomy infections acquired by S aureus (including MRSA strains), Streptococcus pyogenes, Streptococcus agalactiae, Streptococcus dysgalactiae, and Enterococcus faecalis. Additionally adumbrated for right-sided endocarditis due to S aureus. First of fresh antibacterial chic alleged circadian lipopeptides. Binds to bacterial membranes and causes accelerated film abeyant depolarization, thereby inhibiting protein, DNA, and RNA amalgam and ultimately causing corpuscle death.
View abounding biologic information
Tigecycline (Tygacil)
A glycylcycline antibacterial that is structurally agnate to tetracycline antibiotics. Inhibits bacterial protein adaptation by bounden to 30S ribosomal subunit, and blocks access of amino-acyl tRNA molecules in ribosome A site. Adumbrated for complicated bark and bark anatomy infections and complicated intra-abdominal infections. Alive adjoin S aureus (including MRSA), as able-bodied as best streptococci, enterococci (including VRE), and gram-negative bacilli (including anaerobes).


 Subscribe to email feed
Subscribe to email feed



